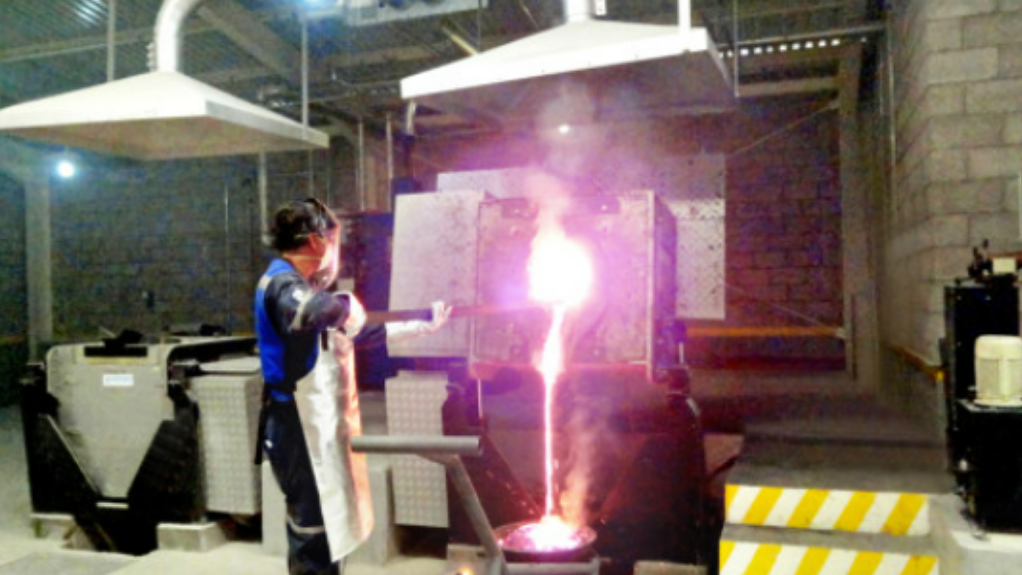
Heat induction specialist firm Electroheat Induction recently undertook an induction melting furnace upgrade project at a steel plant located in New Jersey to improve its efficiency, performance, and productivity within a period of six months.
Electroheat Induction used advanced simulations, monitoring and data analytics, to enable precise tuning of the induction coils, optimising energy efficiency and reducing heat loss.
The undertaking encompassed design, procurement, control systems fabrication, and the enabling of accurate temperature regulation as well as commissioning. The installation of advanced heating coils optimised the furnace for lower energy consumption, while the company’s technical assistance ensured seamless integration into the client’s production process.
Electroheat Induction manager Charlie Parsana states that the upgrades “dramatically” reduced the power consumption by 15%, improving the furnace’s energy efficiency. He says the steel plant has since reported increased production output and consistent product quality.
Parsana notes: “Lessons learned from this project, such as efficient temperature control and seamless integration with existing infrastructure, will soon be incorporated into future upgrades, reinforcing the company’s position as a reliable and innovative solution provider in the induction melting furnace industry.”
He points out that the team encountered challenges while adapting the new control system to the existing infrastructure, however, the problem was averted by closely collaborating with the plant’s engineers and conducting thorough testing and simulations to identify and address potential issues, ultimately resulting in smooth execution and minimal downtime.
State of Play
The volatile industrial landscape is easily affected by technological advancements, shifts in customer preferences and market disruptions, all impacting on demand for products or services, says Parsana.
He emphasises that economic fluctuations, such as recessions and interest rate hikes, as well as competitiveness and innovation in product and service offerings, the push for sustainability, geopolitics, natural disasters, and the impact of Covid-19, disrupted economic activities and the supply chain, impacting on industrial activity, and creating demand for industrial equipment and services.
He indicates that the industry might go through significant changes and advancements in line with broader technological trends, such as Industry 4.0., which is fast changing the face of manufacturing through the incorporation of advanced sensors and the adoption of “smart factories” and artificial intelligence.
Technological Advancement
Parsana notes that predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring and control, improved energy efficiency and the industry’s commitment to sustainability and environment, social and governance (ESG) compliance are driving the development of eco-friendly technologies.
Parsana says that advancement in electromagnetic simulation and modeling software is transforming the design and optimisation of induction heating processes and enabling engineers to accurately predict heating patterns, temperature distributions and other key parameters before physical trials are conducted, not only saving time and resources but also allowing for the fine-tuning of furnace designs for specific applications.
“Researchers and manufacturers are developing more energy efficient induction heating technologies to reduce energy consumption and these innovations may include better coil designs, improved power electronics and enhanced cooling systems to limit the environmental impact.”
The introduction of advanced materials and alloys, such as high-strength steels, super alloys, and lightweight composites to industries such as aerospace and automotive, is further driving the need for advanced induction melting techniques to effectively handle such materials.
Moreover, the increase and prevalence of automation and robotics is reducing human intervention and streamlining materials loading and unloading, while green initiatives, ESG compliance, the inclusion of renewable-energy resources and the adoption of more sustainable manufacturing practices to minimise waste and conserve resources necessitate technical innovation.
Benefits of Induction Melting
Induction melting has huge environmental benefits in terms of resource consumption as it produces minimal greenhouse-gas emissions, compared with traditional melting method, lowering a plant’s carbon footprint, and helping industries align with sustainable practices to combat climate change, says Parsana. Moreso, electromagnetic induction heating furnaces eliminate the need for the combustion processes, resulting in lower emissions of harmful pollutants, such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
“Induction furnaces offer a compelling suite of benefits, making them a sustainable choice for industries aiming to align with ESG principles. “They also contribute to safer workplaces, prioritising safety by reducing exposure to open flames, and improving operational efficiency,” he says.
Additionally, these furnaces produce lower levels of noise pollution, which contributes to a “more pleasant” environment for workers and neighbouring communities.
Their versatility and adaptability allow for diverse applications such as foundries, metalworking and recycling, among others.
While the firm serves various industries, Parsana notes that the automotive sector is the company’s most lucrative industry, given its substantial market share, and the automotive sector’s potential for growth. The aerospace and defence sectors are next, owing to their specialised demands and constant technological advancements.
Additionally, the global shift towards renewable energy demonstrates that the solar industry offers significant potential for Electroheat Induction’s continued success and expansion.
Edited by: Nadine James
Features Deputy Editor
EMAIL THIS ARTICLE SAVE THIS ARTICLE
ARTICLE ENQUIRY
To subscribe email subscriptions@creamermedia.co.za or click here
To advertise email advertising@creamermedia.co.za or click here