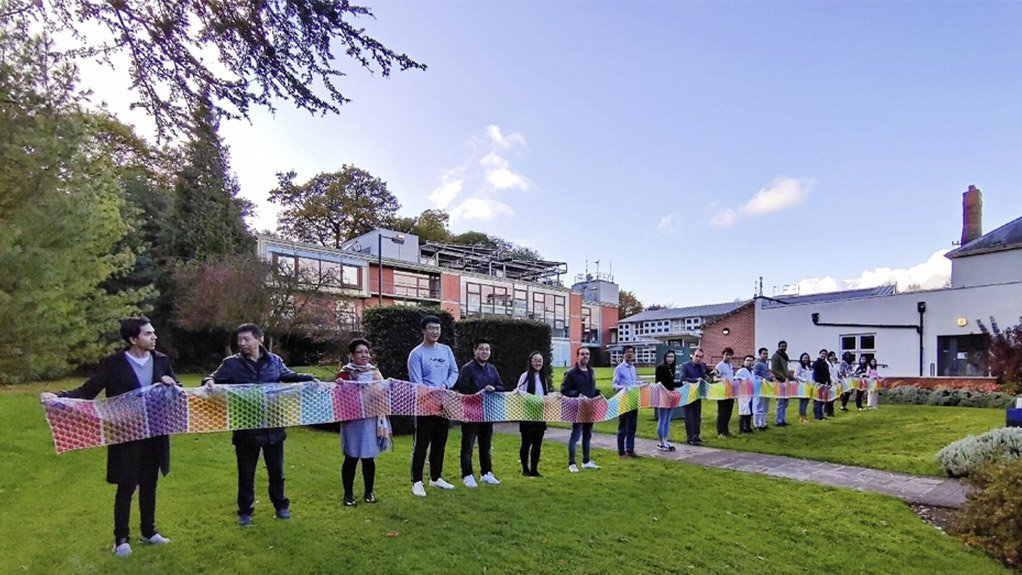
Academics at the University of Nottingham, in the UK have developed thermal energy technology for a range of applications including buildings, greenhouses, cold storage and industrial processes.
The patented ChainStore technology is being promoted by Fellow of the European Academy of Sciences and World Society of Sustainable Technologies president Professor Saffa Riffat and research team member Professor Yijun Yuan.
The world’s electric power requirements are growing rapidly and, according to International Energy Agency estimates, an additional 250 GW of power will be needed annually between now and 2050. Renewable energy technologies including wind, solar and wave can provide clean energy, but these technologies are intermittent, often producing power when a grid utility or users don’t require them. There is therefore an urgent need to develop an efficient and sustainable technology for energy storage, to allow full use of green energy.
Thermal energy storage (TES) is a technology that stores thermal energy using a heating or cooling storage medium so that the stored energy can be used at a later time for heating and cooling applications. TES systems mainly use sensible (e.g. water) and phase change materials (e.g. wax). Current TES technologies are seen as expensive and difficult to integrate into buildings, greenhouses, food storage facilities and other applications.
The newly developed ChainStore technology uses low-cost polymer wraps and composite storage materials that can store large amounts of heat or cooling energy and it can be manufactured into a long chain, extended to hundreds of meters. It can be made into standard products or decorative materials for use in offices, supermarkets, shops or homes.
The technology could assist in harnessing and integrating intermittent renewable power through distributed energy resources and micro-grid systems such as solar photovoltaics and wind energy. It has the potential to provide economic benefits by reducing the overall capital and operation costs of heating or cooling, with systems designed to meet average demand rather than peak demand. It can also support the increase in demand-side management, boosting capacities, reducing life cycle costs, as well as enhancing energy efficiency and reducing carbon dioxide emissions.
The developers state that the technology can be used to improve the reliability and ease of maintenance of heating and cooling sources by serving as an alternative to battery storage and other energy storage systems such as pumped hydro storage.
ChainStore can be used for passive cooling and heating in a range of applications, including sports facilities such as football grounds, where the self-heating technology can be used for defrosting ice on the pitch. It can be charged using renewable energy sources and is said to be inexpensive to install and operate.
ChainStore is seen as a simple, efficient and inexpensive technology that can be produced rapidly on a large scale and offers new opportunities for harnessing solar energy for use in food refrigeration, greenhouses, cooling of buildings and a range of other applications.
Edited by: Creamer Media Reporter
EMAIL THIS ARTICLE SAVE THIS ARTICLE
ARTICLE ENQUIRY
To subscribe email subscriptions@creamermedia.co.za or click here
To advertise email advertising@creamermedia.co.za or click here